Converting NL queries to RDBMS statements
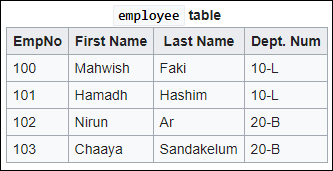
How to convert natural language queries to relational database management system (RDBMS) statements. Problem statement While developing an enterprise search engine, we came into multiple use cases where multiple clients have a large amount of structured data (mainly RDBMS), where they want their non-technical employees to search for expected answers through those databases. For e.g., if there is a table like below: The user can ask “let me know about the department number of Nirun” to get the response “20-B”, instead of writing the following SQL query SELECT DEPT_NUM FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE FIRST_NAME = “NIRUN”; Summarizing these are the requirements break-down Users will ask in a Natural language The query needs to be classified whether to prepare SQL query to hit on DB or to search on free-flowing text documents Users can ask in multiple languages Users should not be expected to remember the exact table/column name of the entire DB User’s query can expect a response from multiple tables or DBs Entire table content may not be available for ingesting; on larger DBs, only the DB schema and sample few rows will be shared by the client for processing For security reasons only the query will be sent as an API to client DB and more than a certain amount of columns and rows cannot be extracted at a time We have decided to divide the solution into two separate phases. Analysis phase Incremental release phase In this first part, only the analysis phase is mentioned. In this phase, we have gone through multiple tools and concepts available over the internet. The following libraries and concepts we have analyzed. Deep learning based solutions Statistical based solutions There are many deep learning based solutions available, a consolidated list you can find here:- https://github.com/salesforce/WikiSQL These models are tested on top of a certain type of data; WikiSQL. WikiSQL are annotated NL query to table data like there is SQuAD data by Stanford for Q&A system. Although some model claim to go beyond 85% accuracy, these are data hungry i.e. some models need to ingest the entire table content data while training, on the other hand, other models need labeled data as per the schema of the table. This approach may work for a PoC, research work and few tables, however, are not scalable and hard to get annotated data. There are few libraries which drew our attention: This is the best library we found. It has some cool features. GPL 3.0 license Take DB dump as input .sql file Only the DB dump is enough, no need for direct access to the whole DB GUI available for ingesting NLP input and SQL query like JSON in output Multi-language supported Customized thesaurus supported i.e. on a way are synonyms Customized stop word supported Most of the nodes are supported It uses TreeTagger, which later says to contact the developers for commercial use. Python 3 only Rule-based query template generation Only working on MySQL DB Entity extraction and schema mapping with the elements Pseudo-column support not there i.e. SYSADMIN, SYSTIMESTAMP etc. Only single table support This is the second best library. License seems like BSD Uses NLTK Tagger which does Tokenizing, PoS Tagging and Lemmatizing A customized RegEx support called, refo Only supports Sparql and MQL, no support for SQL It has not been maintained over a year The customized regex is needed many efforts to understand and customize on need-basis Apache 2.0, easy license to use Parse tree looks good Written in Java, More efforts to customize in Python No good documentation It has not been maintained over a year ln2sql can be leveraged for taking DB dump as input for the initial release. ln2sql’s customized thesaurus and stop word support are also good SQLizer has mentioned a few good practices, those will be checked. For scalability and customization point of view rest, all need to be built as an in-house product. Thanks for your time. Converting NL queries to RDBMS statements
Solution Approach
1. Analysis Phase
Deep learning based solutions
Statistical based solutions
ln2sql
Features
Unavailable features
quepy
Features
Unavailable features
NLIDB
Features
Unavailable features
Possible solutions already built by Non-open source companies
Other Good resources
The final conclusion of the analysis phase